What is Agile Software Development?
Software development methodologies centered round the idea of iterative development, where requirements and solutions evolve through collaboration between self-organizing cross-functional teams.
Why agile?
Agile development is that it enables teams to deliver value faster, with greater quality and predictability, and greater aptitude to respond to change.
Agile Manifesto: 4 Value & 12 Principals (http://agilemanifesto.org)
Values:
- Individuals and interactions over processes and tools
- Working software over comprehensive documentation
- Customer collaboration over contract negotiation
- Responding to change over following a plan
12 Principals:
First Principle (is the Key): Commitment to value delivery: “Highest priority is to satisfy the customer through early and continuous delivery of valuable software.”
What is DevOps ?
DevOps = Development(Dev) + Operation(Ops)
A cultural shift or movement that encourage great collaboration between Dev and Ops team to build (building, testing, and releasing software) quality software more quickly with more reliability
NOTE: DevOps is NOT a “Set of Tools” or Standards
What's the difference between Agile and DevOps?
|
DevOps |
Agile |
|
DevOps is a practice of bringing development and operations teams together |
Agile is an iterative approach that focuses on collaboration, customer feedback and small rapid releases. |
|
DevOps focuses on constant testing and delivery |
Agile process focuses on constant changes |
DevOps Concepts
Build Automation & SCM = Reliable Builds
- Faster Builds – Less manual step, faster execution time
- Consistent – Same way every time means more predictability
- Repeatable – Same code can be rebuild multiple times with same results
- Portable – Can be executed on any machine
Continuous Integration (CI)
- Practice of frequently merging code instead of a mass merge excursive
- Detecting problems earlier
- Should be automated as much as possible
Continues Deployment (CD)
- Practice of continuously maintaining code in deployable state to ensure that the software can be reliably released at any time.
- Actual deployment time is purely a business decision
Continues Delivery (CD)
- A practice of continuously deploying small changes to production
- Deployment is a routine and reliable rollbacks and is automated
- Faster time to market
- Fewer number of changes in each deployment means less risk
Infrastructure as code (Configuration Management)
- Managing infrastructure and provisioning resources through code and automation
- Automatized configuration changes and less configuration drift
- Faster response time
- Reliable
- Repeatable
- Self documenting
Orchestration
- Automation of process/workflows to respond to the infrastructure needs
- Increase demand = create more nodes
- Monitor resources and automate to respond to requirement change
DevOps Periodic Table
https://digital.ai/periodic-table-of-devops-tools
DevOps Practice
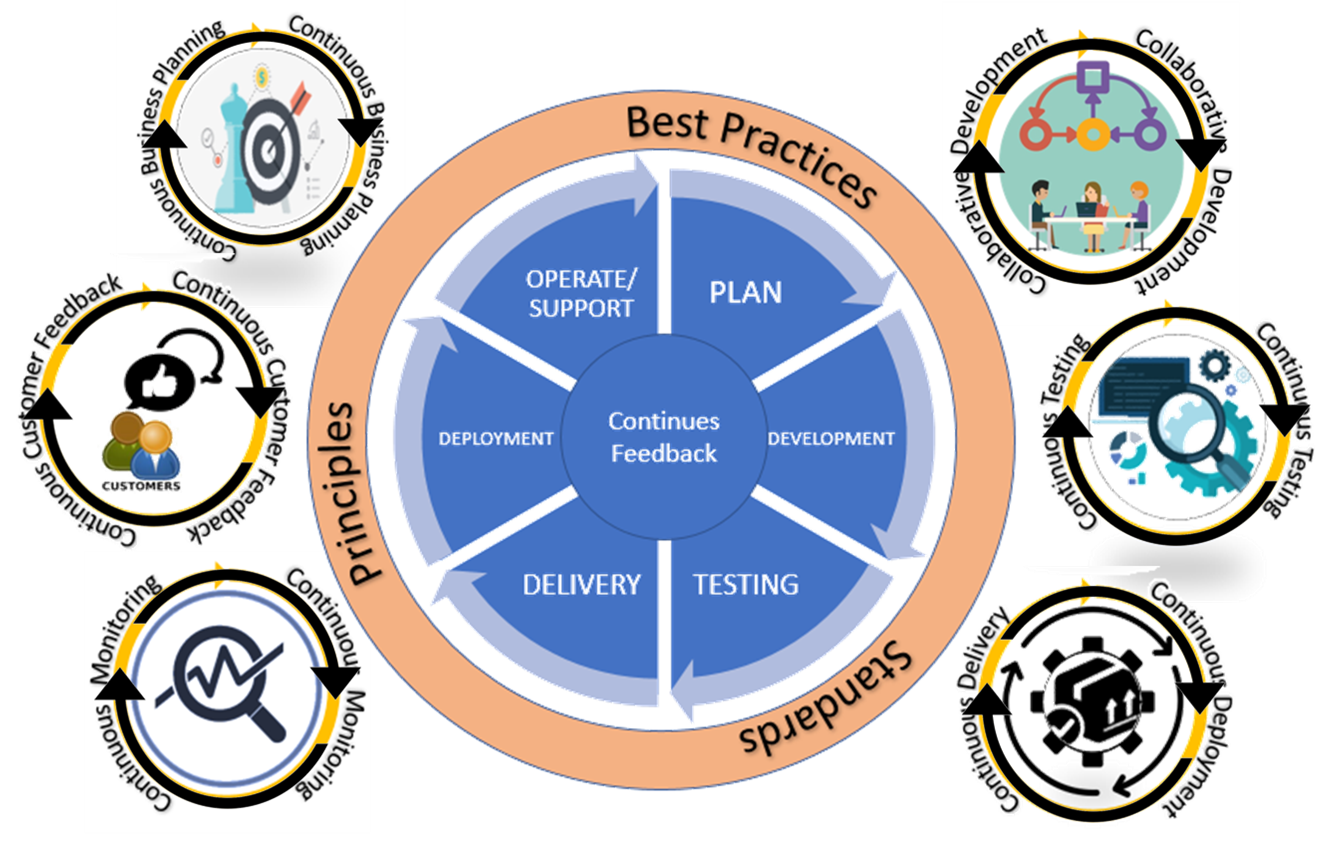
What are some known DevOps practices?
- Canary Releases
- Dark Launches
- Automated Provisioning
- Infrastructure as Code
- Small frequent changes
- Version Control
- Continuous Integration (including automated testing)
- Continuous Delivery / Release Management
- Measuring metrics
Now Lets look at DevOps definition again – (There is No single definition)
“DevOps is a union of people, process, and products to enable continuous delivery of value to end users”
What are some Key DevOps Indicators & Measurements
Velocity KPIs
- MLT (Mean Lead Time)
How long does it take for a bit of code to get built, tested and deployed? - DCR (Daily Change Rate)
Number of changes getting committed to mainline and tested per day. - MTTE (Mean Time To Environment)
How much time it takes developers/testers to bring up a testing environment for verifying each delivered change. - MTTD (Mean Time to Detect)
How much time passes since the original commit of code until the bug it introduces gets detected. - MTTR (Mean Time To Resolve)
How much time it takes to resolve an issue after it’s detected - MTTA (MeanTime To Approve)
How much time it takes to approve and verify a release.
Quality KPIs
- BFR (Build Failure Rate)
Percentage of failed builds - DFR (Deployment Failure Rate)
Percentage of failed deployments - IRFR (Infrastructure-Related Failure Rate)
Percentage of build/deployment failures related to infrastructure issues - RWR (Rework Rate)
Percentage of tickets being reopened - ADR (Automated Detection Rate)
Percentage of defects being detected by automated testing cycles - UWR (Unplanned Work Rate)
Percentage of unplanned issues

